leetcode - 链表 | 字数总计: 3.2k | 阅读时长: 13分钟 | 阅读量:
部分图和题解来自:https://programmercarl.com/
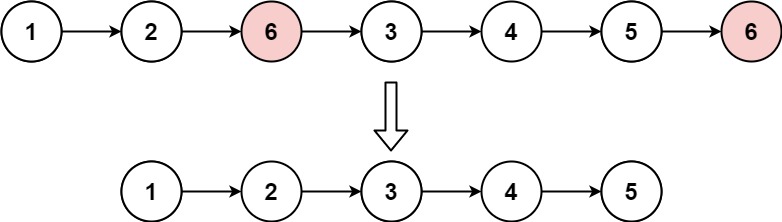
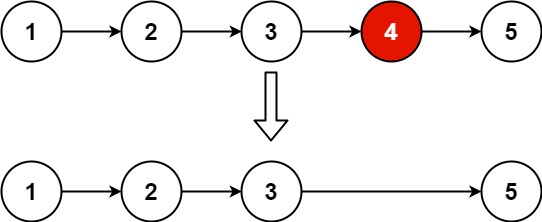
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3:
1 2 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
思路
题解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 var removeElements = function (head, val ) { let retList = new ListNode (0 , head); let current = retList; while (current.next ) { if (current.next .val === val) { current.next = current.next .next ; continue ; } current = current.next ; } return retList.next ; };
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾 。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点 。
deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList(); linkedList.addAtHead(1); linkedList.addAtTail(3); linkedList.addAtIndex(1,2); //链表变为1-> 2-> 3 linkedList.get(1); //返回2 linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); //现在链表是1-> 3 linkedList.get(1); //返回3
思路 添加链表节点:
删除链表节点:
题解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 class Node { constructor (val ){ this .val = val; this .next = null ; } } var MyLinkedList = function ( this .head = null ; this .length = 0 ; }; MyLinkedList .prototype get = function (index ) { if (index < -1 || index >= this .length ) return -1 ; let current = this .head ; let position = 0 ; while (position < index) { current = current.next ; position += 1 ; } return current.val ; }; MyLinkedList .prototype addAtHead = function (val ) { let newNode = new Node (val); newNode.next = this .head ; this .head = newNode; this .length += 1 ; }; MyLinkedList .prototype addAtTail = function (val ) { let newNode = new Node (val); let current; if (this .head === null ) { this .head = newNode; } else { current = this .head ; while (current.next ) { current = current.next ; } current.next = newNode; } this .length += 1 ; }; MyLinkedList .prototype addAtIndex = function (index, val ) { if (index > this .length ) return false ; if (index <= 0 ) { this .addAtHead (val); } else if (index === this .length ) { this .addAtTail (val); } else { let newNode = new Node (val); let current = this .head ; let position = 0 ; let preNode; while (position < index) { preNode = current; current = current.next ; position += 1 ; } newNode.next = current; preNode.next = newNode; this .length += 1 ; } return true ; }; MyLinkedList .prototype deleteAtIndex = function (index ) { if (index < 0 || index >= this .length ) return false ; let preNode; let position = 0 ; let current = this .head ; if (index === 0 ) { this .head = current.next ; } else { while (position < index) { preNode = current; current = current.next ; position += 1 ; } preNode.next = current.next ; } this .length -= 1 ; return current.val ; };
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例一:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例二:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例三:
思路
题解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 var reverseList = function (head ) { if (!head || !head.next ) return head; let preNode = null , current = head, temp = null ; while (current) { temp = current.next ; current.next = preNode; preNode = current; current = temp; } return preNode; }; var reverse = function (pre, head ) { if (!head) return pre; const temp = head.next ; head.next = pre; pre = head return reverse (pre, temp); } var reverseList = function (head ) { return reverse (null , head); }; var reverse = function (head ) { if (!head || !head.next ) return head; const pre = reverse (head.next ); head.next = pre.next ; pre.next = head; return head; } var reverseList = function (head ) { let cur = head; while (cur && cur.next ) { cur = cur.next ; } reverse (head); return cur; };
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例一:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例二:
示例三:
思路
题解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 var swapPairs = function (head ) { let virtualHead = new ListNode (0 ,head), temp = virtualHead; while (temp.next && temp.next .next ) { let current = temp.next .next , preNode = temp.next ; preNode.next = current.next ; current.next = preNode; temp.next = current; temp = preNode; } return virtualHead.next ; };
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例一:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例二:
1 2 输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[]
示例三:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
思路 第一步:
第二步:
第三步:
第四步:
题解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n ) { let virtualHead = new ListNode (0 , head), slow = fast = virtualHead; while (n--) fast = fast.next ; while (fast.next !== null ) { fast = fast.next ; slow = slow.next ; } slow.next = slow.next .next ; return virtualHead.next ; }; var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n ) { let length = 0 ; let current = head; while (current) { length += 1 ; current = current.next ; } if (length === n) { head = head.next ; } else { let position = 0 ; current = head; let preNode; while (position < length - n) { preNode = current; current = current.next ; position += 1 ; } preNode.next = current.next ; } return head; };
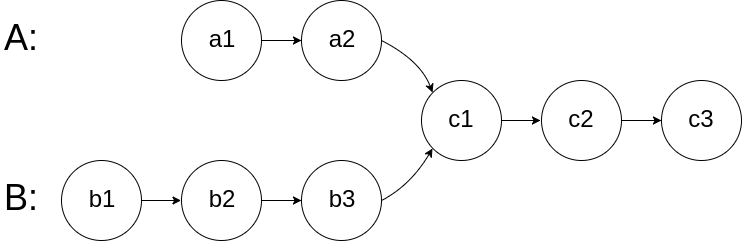
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意 ,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
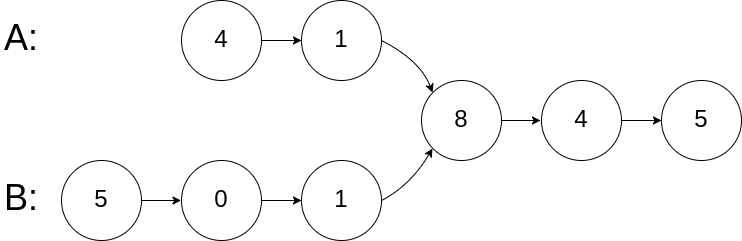
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Intersected at '8' 解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
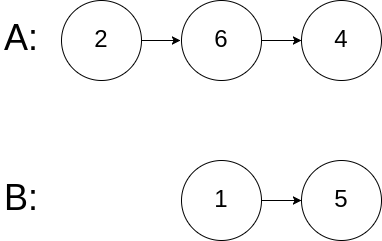
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
思路 题目求求两个链表交点节点的指针,并不是结点值相等,而是指针相等
求出两个链表长度。
将长链表current指针指向和尾部对齐的另一链表的头部current指针。
比较currentA和currentB,不相等则一起向后移动,直至currentA==currentB。
题解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 var getListlength = function (head ) { let length = 0 , current = head; while (current) { length ++; current = current.next ; } return length; } var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB ) { let lenA = getListlength (headA), lenB = getListlength (headB), currentA = headA, currentB = headB; if (lenA < lenB) { [currentA, currentB] = [currentB, currentA]; [lenA, lenB] = [lenB, lenA]; } let n = lenA - lenB; while (n--){ currentA = currentA.next ; } while (currentA && currentA != currentB) { currentA = currentA.next ; currentB = currentB.next ; } return currentA; };
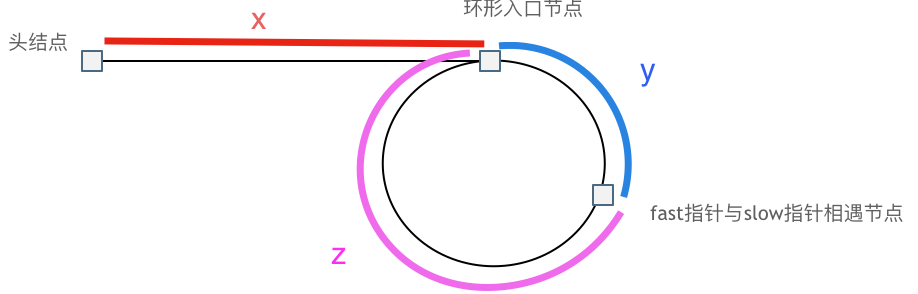
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始) 。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 ,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
1 2 3 输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:返回 null 解释:链表中没有环。
思路 运用快fast慢slow双指针,慢指针每次前进一个节点,快指针前进两个节点
判断链表是否环
因为快指针相对慢指针以1的速度追赶慢指针,所以链表存在环则一定会环中相遇。
如果有环,如何找到这个环的入口
当慢指针第一次进入环中,此时快指针在环中某个位置,如果慢指针走了一圈,则快指针会超过慢指针走了两圈,所以慢指针在环中的第一圈就会和快指针相遇 。
fast指针走了n圈才遇到慢指针,快指针是慢指针2倍速度,则有(x + y) * 2 = x + y + n (y + z),化简得到:x = (n - 1) (y + z) + z,n = 1时,x = z,n != 1时,n圈才相遇,x跟z的距离相等依旧成立 *,所以得到从head和相遇结点以相同1个节点的速度出发的两个指针,相遇结点便是环的入口结点。
题解: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 var detectCycle = function (head ) { if (!head || !head.next ) return null ; let slow = head.next , fast = head.next .next ; while (fast && fast.next && slow != fast) { slow = slow.next ; fast = fast.next .next ; } if (!fast || !fast.next ) return null ; slow = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next ; fast = fast.next ; } return slow; } var detectCycle = function (head ) { if (!head || !head.next ) return null ; let slow = head.next , fast = head.next .next ; while (fast && fast.next ) { slow = slow.next ; fast = fast.next .next ; if (slow == fast) { slow = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next ; fast = fast.next ; } return slow; } } return null ; };